Mechanism of Vitamin C in Hair Loss Prevention and the Superiority of Ethyl Ascorbic Acid
Vitamin C is not a pharmaceutical agent that directly inhibits hormones (like DHT), which are the primary cause of androgenetic alopecia. However, it makes significant contributions to hair loss prevention by playing a multifaceted role in optimizing the scalp environment and supporting follicular function, essential for hair growth and maintenance. While these mechanisms can be attributed to general Vitamin C, ethylated Vitamin C (EVC) offers a distinct advantage in delivery efficiency, leading to more pronounced and practical effects.
The mechanisms and the superiority of ethylated Vitamin C can be broadly categorized into four points:
1. Promotion of Collagen Synthesis: Structural Support and Anchorage of Hair Follicles
-
Collagen as the Follicle’s Foundation: Hair follicles, the factories that produce hair, are deeply embedded in the dermal layer of the skin. Collagen constitutes over 70% of this dermal layer and is the structural component that firmly supports and anchors the hair follicles. Robust collagen ensures stable follicular positioning, preventing easy hair shedding.
-
Vitamin C’s Essential Role: Vitamin C acts as an essential cofactor in the process of collagen synthesis. Without Vitamin C, collagen fibers cannot form a strong and stable structure. A deficiency in Vitamin C impairs collagen synthesis, weakening the dermal layer and reducing the support for hair follicles, thus creating an environment conducive to hair shedding.
-
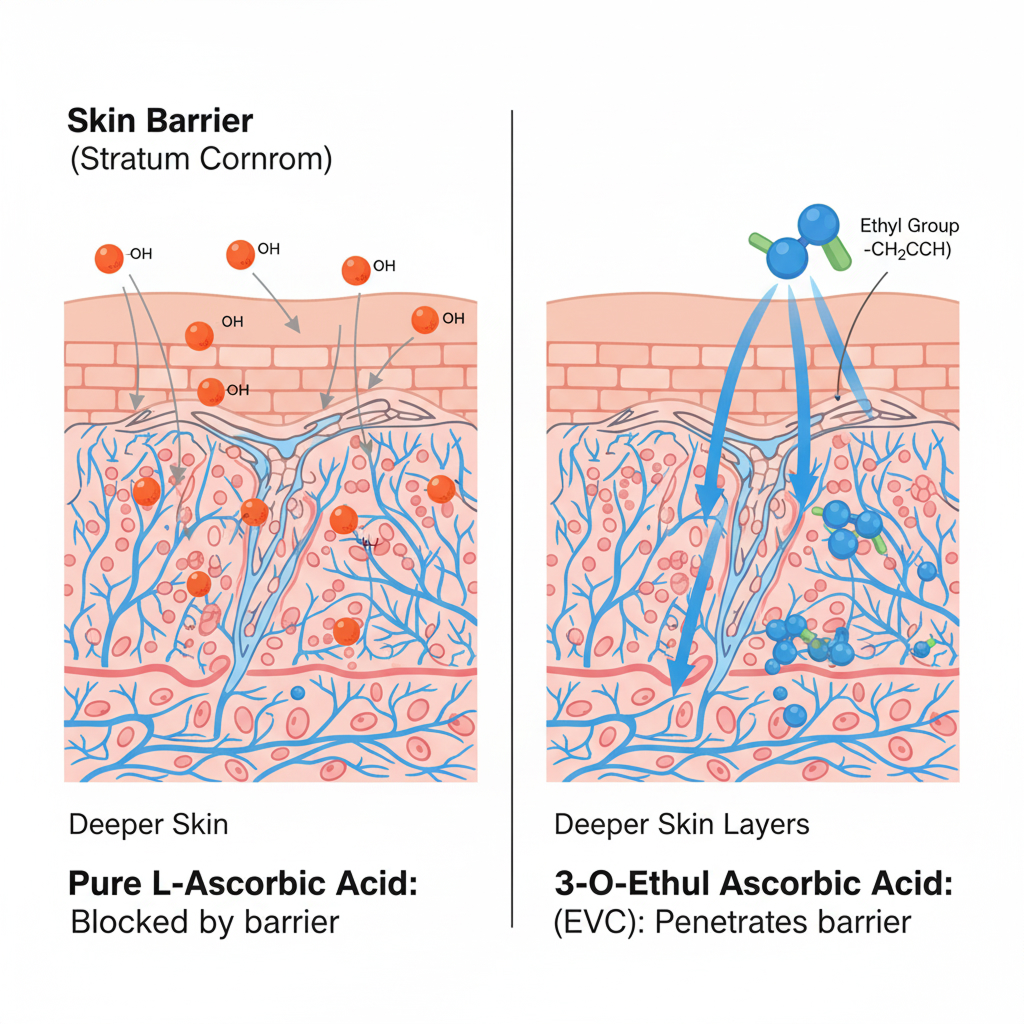
Superiority of EVC: Pure Vitamin C is hydrophilic, making it difficult to penetrate the scalp’s lipid barrier, and it is unstable, oxidizing before it can reach the follicles. In contrast, ethylated Vitamin C (EVC) possesses amphiphilic properties and high stability, allowing it to effectively pass through the scalp barrier and reach the dermal layer surrounding the hair follicles. Once delivered, it is converted into pure Vitamin C by skin enzymes, enabling it to directly act at the key sites for collagen synthesis promotion. This results in a much more efficient strengthening of the follicular structural support compared to unformulated Vitamin C.
-
Mechanism Summary: EVC penetration → Conversion to pure Vitamin C in the skin → Normalization of collagen synthesis → Strengthening of dermal structure → Increased follicular anchorage → Hair loss prevention.
2. Potent Antioxidant Activity: Prevention of Follicle Cell Aging
-
Oxidative Stress and Follicles: The scalp is constantly exposed to oxidative stress from external factors like UV radiation, pollution, and psychological stress. The free radicals generated during this process directly attack and damage follicular cells, including the crucial dermal papilla cells that regulate hair growth and cycling, thereby accelerating their aging.
-
Vitamin C’s Protective Role: Vitamin C, as a powerful antioxidant, stabilizes and neutralizes these free radicals. It protects follicular cells from free radical damage, allowing them to maintain healthy function and continue their normal growth cycle. This is a vital mechanism for preventing premature follicular aging and thus hair loss.
-
Superiority of EVC: Pure Vitamin C is highly unstable, running a significant risk of degradation before it can even reach the scalp. Conversely, ethylated Vitamin C is chemically very stable, allowing it to be delivered deep into the hair follicles in an unoxidized state to effectively neutralize free radicals. This contributes to more efficient protection of follicular cells from oxidative damage, helping to prevent premature aging.
-
Mechanism Summary: Stable EVC penetration → Conversion to pure Vitamin C in the skin → Effective free radical scavenging → Prevention of follicular cell damage and aging → Maintenance of a healthy hair growth cycle.
3. Enhanced Iron Absorption: Blood Circulation and Nutrient Supply to Follicles (for Oral Intake)
-
Iron and Hair Relationship: Iron is a critical component of hemoglobin, which transports oxygen in the blood. Hair follicles, being highly metabolically active, require a substantial supply of oxygen and nutrients. Iron deficiency in the body reduces the blood’s oxygen-carrying capacity, leading to insufficient nutrient supply to the follicles, which can be a direct cause of telogen effluvium (hair thinning and shedding).
-
Vitamin C’s Auxiliary Role: Vitamin C plays a crucial role in significantly enhancing the absorption of non-heme iron found in plant-based foods. Consuming Vitamin C with meals aids in better iron absorption by the body.
-
(Note) This mechanism primarily applies to orally ingested Vitamin C. Since ethylated Vitamin C is primarily used for topical application, this mechanism should be understood as pertaining to Vitamin C consumption in general.
-
4. Maintenance of Vascular Health: Ensuring Nutrient Supply Pathways
-
Importance of Capillaries: Capillaries are connected to the base of the hair follicle, providing a pathway for nutrient and oxygen supply. Healthy and strong capillaries ensure efficient nutrient delivery.
-
Vitamin C and Vascular Elasticity: Vitamin C contributes not only to the synthesis of collagen, which forms blood vessel walls, but also to maintaining the elasticity and overall health of blood vessels. Healthy scalp vasculature is like maintaining robust “pipelines” that supply nutrients to the hair follicles.
-
Superiority of EVC: Topically applied ethylated Vitamin C, upon reaching the dermal layer around blood vessels and converting to pure Vitamin C, can locally promote collagen synthesis for vessel walls and enhance antioxidant protection of the perivascular tissues. This indirectly supports the health of scalp microvasculature, contributing to more efficient nutrient delivery to the hair follicles.
-
Mechanism Summary: EVC penetration and activation → Support for perivascular collagen synthesis and antioxidant protection → Maintenance of healthy scalp microvasculature → Secured nutrient supply pathways to follicles → Optimized hair growth environment.
In conclusion, Vitamin C contributes to hair loss prevention through multiple mechanisms: strengthening follicular anchorage via collagen synthesis, protecting follicular cells through antioxidant action, and (when ingested) promoting iron absorption and maintaining vascular health. Crucially, ethylated Vitamin C, due to its superior stability and skin permeability, can effectively deliver the active ingredient to the peripapillary regions of the hair follicle that pure Vitamin C struggles to reach. This allows for a more substantial and superior effect in hair loss prevention and healthy hair growth when applied topically, compared to conventional Vitamin C.




